ESD Coating
Product Description
The Importance of ESD Coating in the Semiconductor Industry
ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) is a critical concern in the semiconductor industry because static electricity can cause permanent damage to sensitive electronic components and equipment. ESD Coating, as an electrostatic protection technology, holds significant value and necessity in semiconductor manufacturing and testing processes.
Common Causes of Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)
Electrostatic discharge typically occurs due to the accumulation and release of static charges. Below are common causes of ESD:
- Triboelectric Charging: Static electricity builds up when two different materials come into contact and then separate, causing electron transfer and static charge accumulation.
- Contact and Separation: Brief contact between objects followed by separation can generate static electricity.
- Charge Induction: When a conductive object approaches a charged object, it induces a charge distribution that can result in electrostatic discharge.
- Material Properties: Certain materials, such as plastic, glass, and rubber, are highly insulative and prone to static charge accumulation.
- Environmental Conditions: Low humidity or temperature fluctuations can exacerbate static charge generation.
- Rapid Movement or Flow: Fast-moving objects or materials can generate static charges due to friction with their surroundings.
- Poor Grounding: When conductors or equipment are not properly grounded, static charges cannot dissipate effectively, leading to accumulation and potential discharge.
- Operational Behavior: Handling objects without anti-static equipment (e.g., wrist straps, footwear) can result in charge buildup.
- Handling of ESD-Sensitive Components: Friction or contact during the handling of electronic components, such as IC chips or circuit boards, can generate static charges.
- Static from Electric Fields: In environments with strong electric fields, materials can accumulate static charges through field induction.
Key Applications of ESD Protection
ESD protection is crucial in environments involving static-sensitive electronic components and manufacturing processes. Below are its primary application scenarios, particularly in the semiconductor industry:
-
Chip Manufacturing and Testing
- During the semiconductor manufacturing process, electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage sensitive electronic components, such as integrated circuits and transistors.
-
Wafer Testing and Final Testing
- In wafer testing and final testing stages, ESD protection is essential to prevent damage to components and ensure accurate test results.
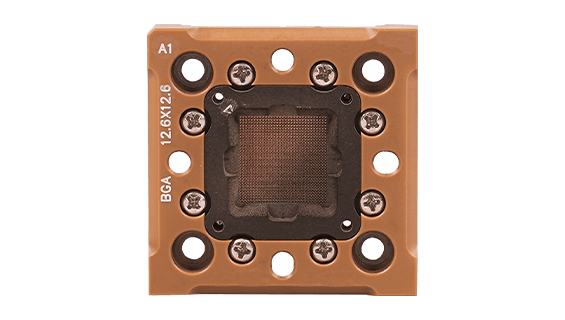
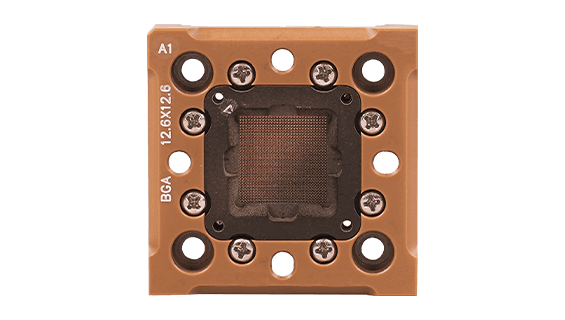
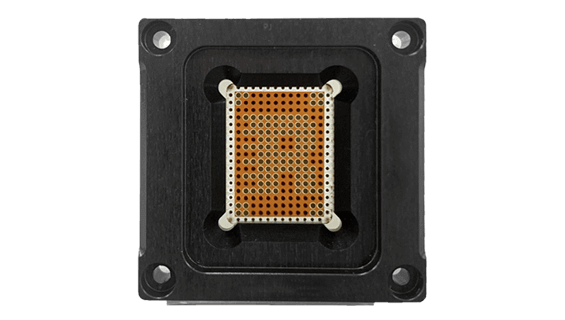
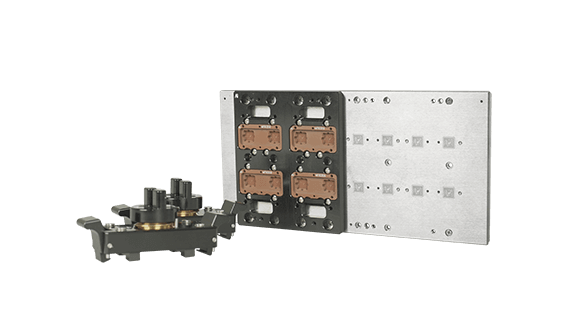
- Products such as semiconductor test fixtures and probe heads commonly use ESD Coating to reduce static charge buildup and avoid disruptions caused by static discharge during testing.
Materials Used in ESD Coating
The core of ESD Coating lies in selecting the appropriate coating materials, which must possess antistatic, static dissipative, or conductive properties to effectively control static charge generation and accumulation in various environments. Based on application scenarios and performance requirements, the commonly used ESD Coating materials are as follows:
-
Polymer Coatings
- Polymers are the most commonly used base materials in ESD Coatings.
- They achieve static dissipative functionality by incorporating antistatic agents or conductive fillers.
-
Conductive Filler Coatings
- Conductive fillers are added to the base material to enhance the static dissipative properties of the coating.
- Suitable for applications requiring improved electrical conductivity.
-
Metal Oxide Coatings
- Transparent Conductive Oxide (TCO) coatings are used for applications where transparency must be maintained.
- Commonly applied in displays or optical devices requiring static control.
-
Static Dissipative Paints
- Specially designed for static control, these paints have a surface resistance range typically between 10⁶ to 10⁹ Ω/sq.
- They balance conductivity and dissipation for effective ESD management.
-
Nanomaterial Coatings
- The introduction of nanotechnology enhances the performance of ESD coatings.
- Nano-scale fillers provide superior conductivity and durability compared to traditional materials.
-
Surface Treatment Technologies
- In addition to coating materials, certain surface treatment techniques can further enhance ESD control.
- These treatments improve adhesion, durability, and overall effectiveness of the ESD coating.
Solutions Provided by Pin-Jet in ESD Protection
-
ESD Coating
- Features: ESD coating is applied to the surfaces of test fixtures or sockets, effectively reducing static accumulation and preventing damage to components from electrostatic discharge.
-
Advantages:
Enhances safety during the testing process.
Extends the lifespan of testing equipment.
-
Cleaning Tools
- Product: Tools such as the Clean Pad, specifically designed for cleaning test probes (Pogo Pins).
-
Advantages:
Maintains the cleanliness of probes without damaging the gold plating.
Ensures accuracy and stability in testing.
-
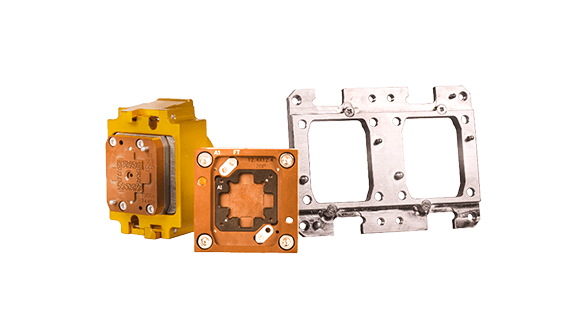
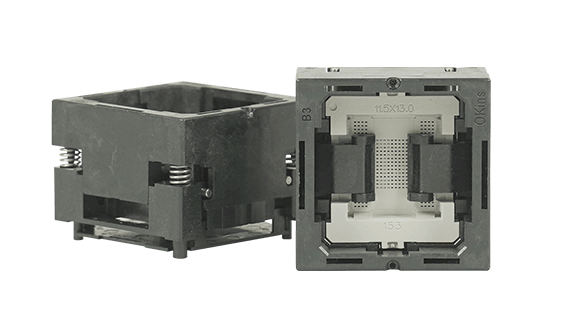
IC Test Sockets
- Products: Includes POP Sockets and Final Test Sockets, and other socket solutions.
-
Advantages:
Designed to meet high-frequency and high-speed testing requirements.
Incorporates ESD protection to ensure the safety and accuracy of the testing process.
Test Result :
Clean Pad Performance: Extensive tests have confirmed that Pin-Jet 's Clean Pad effectively cleans Pogo Pins without damaging the gold plating.
ESD Protection: All Pin-Jet 's products undergo rigorous ESD protection testing, ensuring reliable static protection in real-world applications.
Testing Methods to Evaluate ESD Protection Effectiveness
- Contact Discharge Test: An ESD simulator directly contacts the test object to apply a controlled electrostatic discharge.
- Air Discharge Test: The ESD simulator is brought close to the test object until a discharge occurs through the air.
- Human Body Model (HBM) Test: Simulates electrostatic discharge caused by a charged human body touching an electronic component.
- Machine Model (MM) Test: Simulates electrostatic discharge caused by a charged machine or equipment touching an electronic component.
- Charged Device Model (CDM) Test: Simulates the scenario where a component becomes charged and then discharges upon contact with a grounded object.
FAQ About ESD Coating
1. What is the effective lifespan of ESD Coating?
Customer Question:
"How long does the protective effect of ESD Coating last? How often does it need to be reapplied?"
Response:
"The effective lifespan of ESD Coating depends on the materials used and environmental conditions such as humidity, temperature, and friction frequency. Our coatings are designed with durable materials and typically last for several years under normal operating conditions. Regular surface resistivity checks can help determine whether reapplication is necessary in a timely manner."
2. How to Perform Maintenance and Cleaning?
Customer Question:"Does the coating surface require special cleaning methods?"
Response:
"To prolong the lifespan of ESD Coating, we recommend gently wiping the surface with non-alcoholic, non-corrosive cleaning agents. Avoid using sharp objects or abrasive cleaning methods. We provide a cleaning and maintenance guide to help you maintain the optimal performance of the coating."
3. Can the Coating Be Repaired?
Customer Question:"If the coating is damaged, can it be repaired?"
Response:
"Yes, our ESD Coating can be locally repaired to avoid the waste of a full reapplication. We provide repair kits and detailed instructions to ensure that the protective performance after repair matches that of the original coating."
4. Does the Product Meet International Standards?
Customer Question:"Does the ESD Coating comply with international standards such as ANSI/ESD S20.20 or IEC 61340?"
Response:
"Our products fully comply with international standards such as ANSI/ESD S20.20 and IEC 61340 and have been certified by third-party testing agencies. You can confidently apply them in any static protection environment requiring compliance with these standards."
Product Specification
規格:1*105Ω≦R<1*109Ω
MORE PRODUCTS
Contact Us Now
Complete online forms and Pin-Jet will have representatives to help you with professional services